The complete FEIE Standard Deduction overview for first-time expats
Wiki Article
Comprehending the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion and Its Influence On Your Typical Deduction
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) supplies considerable benefits for migrants, permitting them to exclude a part of their foreign-earned earnings from united state taxation. Nonetheless, declaring the FEIE can complicate one's tax obligation circumstance, specifically relating to the conventional deduction. Understanding this interaction is crucial for individuals living abroad. As expatriates navigate these complexities, they have to consider exactly how their options influence their overall tax liability. What methods can they employ to optimize their financial results?What Is the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE)?
The Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) functions as an important tax benefit for U.S. citizens and resident aliens functioning abroad. This provision enables qualified people to leave out a substantial section of their foreign-earned income from united state taxes, effectively decreasing their general tax concern. The FEIE aims to ease the monetary pressure on expatriates and urges Americans to seek job opportunity in international markets. The exemption relates to salaries, salaries, and expert charges gained while living in an international nation. The optimal exemption quantity is changed every year for inflation, guaranteeing that it remains pertinent to present economic problems. By making use of the FEIE, expatriates can maintain even more of their revenue, promoting financial security while living overseas. On the whole, the FEIE plays an important duty in shaping the financial landscape for Americans abroad, assisting in a smoother shift to international work environments and advertising economic involvement on a worldwide scale.Qualification Demands for the FEIE
Eligibility for the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) rests upon meeting certain standards established by the Internal Earnings Service (INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE) Largely, individuals need to be united state people or resident aliens that gain earnings while staying in a foreign country. To certify, they need to satisfy a couple of primary tests: the Physical Existence Examination or the Bona Fide Home Test.The Physical Presence Test calls for individuals to be literally present in an international nation for a minimum of 330 complete days within a 12-month period - FEIE Standard Deduction. Alternatively, the Bona Fide Home Examination necessitates that individuals develop residency in a foreign country for an uninterrupted period that consists of a whole tax year
Furthermore, the earnings must be originated from personal services done in the international nation. Meeting these requirements allows taxpayers to exclude a considerable section of their foreign-earned income from united state taxes, consequently reducing their overall tax obligation responsibility.
How to Assert the FEIE
To begin the process, people must collect files that confirm their foreign incomes, such as pay stubs, income tax return from international nations, and any appropriate work agreements. It is essential to assure all income declared under the FEIE is gained from foreign resources and fulfills the needed limits.
Furthermore, taxpayers must think about submitting target dates and any type of possible expansions. Declaring the FEIE properly not just assists in reducing tax obligation responsibility but also guarantees compliance with internal revenue service policies. Correct documents and adherence to guidelines are important for an effective case of the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion.
The Communication Between FEIE and Typical Reduction
The interaction in between the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) and the typical deduction is a necessary element of tax obligation planning for expatriates. Comprehending the standard concepts of FEIE, along with the constraints of the conventional deduction, can considerably influence tax obligation declaring approaches. This section will check out these aspects and their ramifications for taxpayers living abroad.FEIE Fundamentals Described
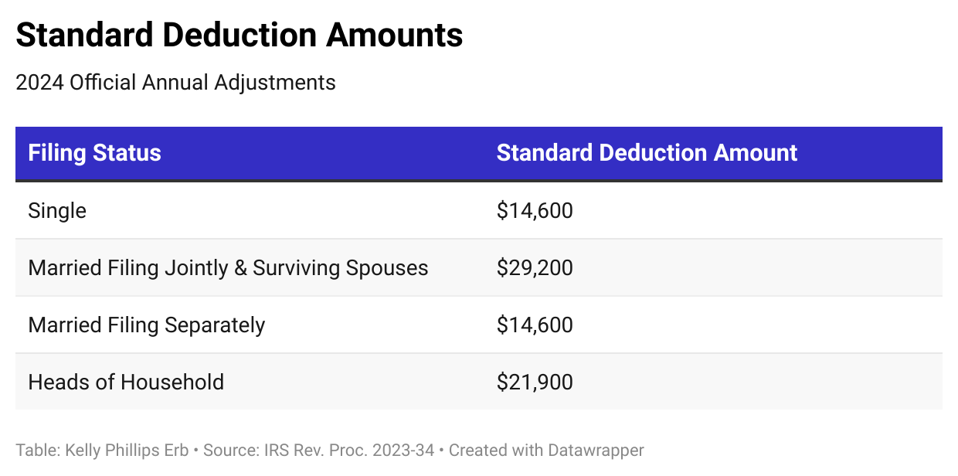
While lots of migrants seek to decrease their tax concern, understanding the interaction between the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) and the common deduction is crucial. The FEIE allows united state people and resident aliens living abroad to exclude a certain quantity of international made revenue from united state tax. This exclusion can considerably reduce taxed earnings, potentially influencing qualification for various other deductions, such as the conventional reduction. Extremely, people who declare the FEIE can not additionally take the basic reduction versus the omitted revenue. Consequently, expatriates must meticulously review their overall revenue and deductions to optimize their tax circumstance. Awareness of these communications can bring about more educated monetary decisions and far better tax techniques for expatriates steering via their unique conditions.Standard Deduction Limitations
Recognizing the restrictions of the typical deduction in connection to the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) is necessary for expatriates maneuvering their tax obligation duties. While the FEIE enables certifying people to leave out a specific amount of foreign-earned earnings from U.S. taxation, it can impact the basic deduction they are eligible to claim. Especially, taxpayers that assert the FEIE can not also claim the common deduction on that omitted income. Additionally, if a migrant's complete earnings drops below the common reduction threshold, they may not benefit from it at all. This interplay requires cautious preparation to optimize tax benefits, as underutilizing the typical deduction can bring about greater gross income and raised tax obligation. Comprehending these constraints is important for effective tax approach.Tax Obligation Declaring Effects
Navigating the tax filing effects of the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) calls for cautious consideration of how it engages with the standard deduction. Taxpayers using the FEIE can exclude a significant section of their foreign-earned earnings, yet this exclusion affects their qualification for the conventional reduction. Specifically, if a private cases the FEIE, they can linked here not likewise declare the conventional deduction for that revenue. This can result in a lower total tax obligation but may make complex the filing procedure. Furthermore, taxpayers must ensure compliance with internal revenue service needs when submitting Kind 2555 for the FEIE. Comprehending these interactions is essential for optimizing tax benefits while staying clear of possible risks in the filing process. Mindful preparation can make best use of advantages and lessen responsibilities.Potential Tax Obligation Effects of Making Use Of the FEIE
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) supplies substantial tax obligation advantages for united state people functioning abroad, but it likewise comes with possible implications that require cautious consideration. One significant effect is the influence on qualification for sure tax credit scores and deductions. By choosing to make use of the FEIE, taxpayers may inadvertently minimize their adjusted gross revenue, which can limit accessibility to credit scores like the Earned Income Tax obligation Credit score or minimize the quantity of common reduction readily available.
Furthermore, individuals that make use of the FEIE may deal with issues when going back to the united state tax obligation system, particularly worrying the taxes of future revenue. The exemption applies only to earned income, meaning other revenue kinds, such as dividends or rate of interest, remain taxed. This distinction requires meticulous record-keeping to guarantee conformity. Finally, the FEIE might affect state tax obligations, as some states do not identify the exclusion and might tax all income earned by their homeowners, despite where it is earned.
Tips for Maximizing Your Tax Benefits While Abroad
While working abroad can be enriching, it additionally presents distinct chances to optimize tax obligation benefits. To maximize these benefits, people should initially determine their eligibility for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) and take into consideration the physical presence test or the authentic home examination. Keeping in-depth documents of all income earned and expenses incurred while overseas is vital. This paperwork supports insurance claims for reductions and credit reports.Additionally, understanding the tax obligation treaties in between the United States and the host country can assist avoid dual taxes. Individuals must also discover payments to tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual retirement accounts, which may give additional deductions.

Lastly, speaking with a tax obligation expert focusing on expatriate tax legislation can offer customized strategies and assurance conformity with both U.S. and international tax commitments. By taking these steps, migrants can successfully enhance their monetary scenario while living abroad.
Frequently Asked Concerns
Can I Make Use Of FEIE if I Benefit an International Government?
Yes, an individual can utilize the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) while helping a foreign government, offered they meet the requisite problems outlined by the internal revenue service, consisting of the physical presence or bona fide home tests.
Does FEIE Relate To Self-Employment Income?
The Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) does use to self-employment earnings, supplied the private meets the necessary needs. Eligible self-employed people can omit certifying income earned while staying in a foreign nation from tax.What happens if My International Income Goes Beyond the FEIE Limitation?
The excess amount may be subject to United state taxation useful site if foreign earnings surpasses the FEIE restriction. Taxpayers should report and pay tax obligations on the revenue over the exemption threshold while still profiting from the exemption.Can I Declare the FEIE and Itemize Reductions?
Yes, people can assert the Foreign Earned go right here Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) while also making a list of deductions. However, they need to know that asserting the FEIE may impact the availability of particular itemized deductions on their income tax return.How Does FEIE Affect My State Tax Commitments?
The Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption can lower state tax obligation obligations, as many states adhere to government standards. Individual state regulations differ, so it's vital to get in touch with state tax obligation guidelines for specific effects on tax responsibilities.The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) supplies considerable benefits for migrants, enabling them to leave out a section of their foreign-earned earnings from U.S. taxes. While many expatriates look for to minimize their tax problem, recognizing the interaction between the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) and the standard deduction is important. Recognizing the limitations of the typical reduction in connection to the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) is crucial for migrants navigating their tax obligation obligations. The exemption uses just to earned earnings, meaning other revenue types, such as dividends or passion, remain taxed. The Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) does use to self-employment income, supplied the individual satisfies the needed needs.
Report this wiki page